- Full AVMA-CVTEA accreditation, allowing graduates to qualify for the VTNE examination.
- Study online, at your own pace, wherever you are.
- Receive ongoing support from our Veterinary Academy Team.
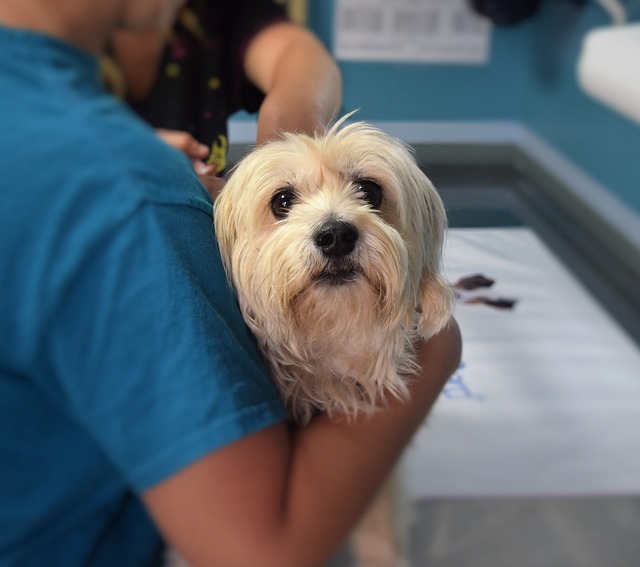
As an animal lover, you might think about becoming a veterinary technician (vet tech).
But you may have no idea what the job entails.
Vet techs work in many different settings, such as:
- Labs
- Veterinary offices
- Colleges
But all vet techs have one thing in common.
You all love animals, and you want to help them in any way possible.
- Job Description
- Salary
- How to Become
- Education
- Certification & Licensing
- Popular Programs
- Job Outlook
- Should You Become
- FAQs
- Info by State
- Similar Careers
What Does a Vet Tech Do?
A vet tech’s typical workday varies from day to day and workplace to workplace.
As a vet tech, you will be:
- Helping the animals
- Advising the animals’ owners
- Assisting the veterinarian
Duties
Here are the duties you will perform:
- Give the animals necessary medicines and vaccines
- Bathe animals
- Collect a variety of different samples
- Observe the conditions and behaviors of animals
- Perform lab examinations
- Provide nursing care and first aid
- Assist the veterinarians during procedures and exams
- Do diagnostic tests like fecal exams, blood tests, urinalysis, x-rays, etc.
- IV catheter and phlebotomy placement
- Prepare the animals for surgery, helping during and after the surgery
- Educate owners about the welfare and proper care of their pets
- Make sure that animals in the lab are treated humanely
- Provide injured or sick animals with emergency care when necessary
How Much Does A Vet Tech Earn
One question many people ask is how much this job pays.
The pay that you receive changes depending on a variety of factors, such as:
- Specialization
- Work environment
- Amount of schooling
- Experience
The national annual average salary ranges from $21,890 to $47,410.
Average National Salary: $32,490
Salary Information by State
| State | Employed | Avg. Annual Salary | Avg. Hourly Pay | Top 10% Annual Salary | Bottom 10% Annual Salary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 2,030 | $33,750 | $16.22 | $43,710 | $27,040 |
| Alaska | 290 | $45,510 | $21.88 | $57,410 | $34,440 |
| Arizona | 3,160 | $41,410 | $19.91 | $48,820 | $34,540 |
| Arkansas | 220 | $34,450 | $16.56 | $41,970 | $27,540 |
| California | 9,320 | $55,740 | $26.80 | $73,330 | $39,280 |
| Colorado | 4,400 | $46,240 | $22.23 | $59,160 | $35,880 |
| Connecticut | 1,880 | $48,980 | $23.55 | $61,560 | $37,240 |
| Delaware | 680 | $42,630 | $20.50 | $60,800 | $29,880 |
| District of Columbia | 140 | $56,420 | $27.13 | $76,030 | $39,240 |
| Florida | 10,310 | $41,640 | $20.02 | $54,300 | $30,270 |
| Georgia | 2,840 | $40,390 | $19.42 | $49,310 | $29,110 |
| Hawaii | 320 | $44,150 | $21.23 | $66,640 | $28,420 |
| Idaho | 740 | $38,400 | $18.46 | $45,930 | $30,610 |
| Illinois | 4,450 | $44,670 | $21.47 | $60,470 | $31,770 |
| Indiana | 2,430 | $41,280 | $19.85 | $48,720 | $31,350 |
| Iowa | 1,050 | $41,530 | $19.97 | $58,640 | $31,390 |
| Kansas | 1,070 | $38,940 | $18.72 | $49,200 | $27,450 |
| Kentucky | 1,920 | $35,370 | $17.01 | $45,760 | $26,960 |
| Louisiana | 1,530 | $31,810 | $15.30 | $41,690 | $23,430 |
| Maine | 860 | $47,560 | $22.86 | $58,800 | $37,480 |
| Maryland | 2,690 | $45,160 | $21.71 | $59,670 | $33,930 |
| Massachusetts | 3,190 | $48,270 | $23.21 | $59,120 | $36,830 |
| Michigan | 3,100 | $46,310 | $22.26 | $57,310 | $36,210 |
| Minnesota | 4,070 | $46,080 | $22.15 | $57,320 | $36,820 |
| Mississippi | 1,010 | $33,990 | $16.34 | $44,090 | $22,350 |
| Missouri | 2,000 | $38,600 | $18.56 | $49,520 | $28,480 |
| Montana | 650 | $39,590 | $19.03 | $48,930 | $30,630 |
| Nebraska | 750 | $40,040 | $19.25 | $48,830 | $29,830 |
| Nevada | 540 | $46,830 | $22.51 | $57,720 | $38,290 |
| New Hampshire | 1,020 | $46,860 | $22.53 | $60,550 | $36,820 |
| New Jersey | 3,660 | $47,100 | $22.64 | $59,950 | $36,390 |
| New Mexico | 800 | $39,070 | $18.78 | $50,690 | $28,630 |
| New York | 5,220 | $55,540 | $26.70 | $76,660 | $39,680 |
| North Carolina | 3,570 | $44,580 | $21.43 | $59,270 | $31,710 |
| North Dakota | 310 | $40,540 | $19.49 | $47,140 | $28,700 |
| Ohio | 4,320 | $40,660 | $19.55 | $49,430 | $30,900 |
| Oklahoma | 960 | $36,540 | $17.57 | $47,230 | $28,600 |
| Oregon | 1,810 | $44,810 | $21.54 | $57,900 | $31,500 |
| Pennsylvania | 5,190 | $44,250 | $21.27 | $59,570 | $31,150 |
| Rhode Island | 450 | $42,510 | $20.44 | $60,700 | $30,090 |
| South Carolina | 1,940 | $41,460 | $19.93 | $56,590 | $30,770 |
| South Dakota | 360 | $41,200 | $19.81 | $45,830 | $36,040 |
| Tennessee | 1,720 | $38,250 | $18.39 | $49,850 | $28,820 |
| Texas | 12,980 | $37,560 | $18.06 | $48,980 | $27,540 |
| Utah | 1,370 | $39,370 | $18.93 | $47,030 | $30,310 |
| Vermont | 430 | $43,080 | $20.71 | $47,780 | $37,370 |
| Virginia | 2,400 | $50,980 | $24.51 | $64,440 | $35,910 |
| Washington | 2,570 | $54,460 | $26.18 | $64,430 | $43,410 |
| West Virginia | 450 | $33,910 | $16.30 | $45,590 | $24,580 |
| Wisconsin | 2,530 | $43,770 | $21.04 | $56,550 | $34,660 |
| Wyoming | 300 | $35,600 | $17.11 | $46,590 | $21,290 |
| Puerto Rico | 450 | $28,710 | $13.80 | $47,450 | $22,430 |
Annual Average Salary: Top 10 States
The top earning state in the field is District of Columbia, where the average salary is $56,420.
These are the top 10 earning states in the field:
* Employment conditions in your area may vary.
Step-by-Step Guide to Becoming a Vet Tech
Step 1 Graduate From High School or Get Your GED
Before anything else, you will need to get your high school diploma or GED equivalent.
It allows you to take science and health courses necessary to study a vet tech program.
For instance, biology and chemistry.
Pro Tip: Learning a foreign language is handy when interacting with foreign clients.
Step 2 Earn Your Associate’s Degree
One advantage of having an associate’s degree is that it lands you a job as soon as you graduate.
So when choosing a school, make sure it’s an American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) accredited one first.
You can go to community colleges as they often have excellent vet tech training programs.
And typically, training lasts up to two years.
This is enough to get you into the entry-level position.
Step 3 Consider Getting a Specialization
Having a vet tech specialization means better job prospects.
Here are some specializations you can consider taking:
- Dentistry
- Equine nursing
- Clinical practice
- Anesthesia and analgesia
- Emergency and critical care
Step 4 Hone Your Soft Skills
Aside from the hard skills, you must also develop your soft skills.
As a vet tech, you must have:
- Good communication skills
- Interpersonal skills
- Empathy
These ensure you can interact well with people, especially with your patient’s owners.
Step 5 Get Your Certifications and Licenses
Every vet tech needs to either be:
- Certified
- Licensed
- Registered
The requirements vary per state, but most vet techs have to pass an exam, which has the following sections:
- Written
- Oral
- Demonstrative
Passing this will prove to the state that you have the aptitude for animal care.
Step 6 Complete the On-The-Job Training
Most programs require you to intern with a licensed vet to get first-hand experience.
This usually means a shorter training period for you.
While in some cases, you will get the training after you’ve found employment.
Nonetheless, during that time, you must immerse yourself and complete the training satisfactorily.
Step 7 Think About Career Advancement Opportunities
The more experience you gain, the more opportunities you will encounter.
For instance, getting a promotion to oversee veterinary assistants and junior technicians.
Career opportunities also arise from:
- Continuing education
- Participating in conventions and events
Education Needed to Become a Vet Tech
To get started on your vet tech journey, you first have to enroll in an AVMA-accredited school.
Doing so means that you will get the quality education and extensive training necessary to be a vet tech.
Here are some of those accredited schools in the U.S. you can check out:
- Auburn University
- University of Arizona
- University of California
- Colorado State University
- University of Florida
- University of Georgia
- Purdue University
- Cornell University
- Texas Tech University
- Washington State University
For a full list of accredited schools, visit AVMA’s website.
Once you’ve chosen a school, then you can proceed to your studies and hold an associate’s degree.
Pro Tip: Holding an associate’s degree creates a continuing education opportunity in veterinary studies.
The course program lasts for about two years.
And after successful completion, you will be officially recognized as a vet tech.
You’re now able to apply for a job and do entry-level duties.
Here’s a video from a seasoned vet tech to give you some insights on areas you should know about.
Video About The Career
Certification & Licensing
Depending on the state where you currently live, you may be a:
- Licensed Veterinary Technician, which is awarded by the state’s veterinary medical board
- Certified Veterinary Technician, which you obtain through a professional or private program
- Registered Veterinary Technician, which is given by government agencies
If you live anywhere but Alaska, California, or Wisconsin, you’ll need to:
- Complete a state-approved program
- Pass the exam
State tests are usually waived if you’ve passed the Veterinary Technician National Exam.
It’s a 200-question exam that will measure your competency at the entry level.
This exam covers topics such as:
- Animal care and nursing
- Dentistry procedures
- Lab procedures
And if you’re planning to engage in research, you’ll also need certification from the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science.
They have three certification levels.
- Assistant Laboratory Technician
- Laboratory Animal Technician
- Laboratory Animal Technologist
Average Training Program Duration: 2-3 Years
Popular Programs
Get your accredited and budget-friendly associate degree or career diploma entirely online!
Veterinary AssistantVeterinary TechnicianVet Office ManagerDog ObediencePet GroomingSponsored Online Programs.Job Outlook and Growth for Vet Techs
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job outlook for vet techs is expected to grow up to 15% from 2020 to 2030.
This rate is much higher compared to other occupations on average.
Moreover, this number means that there’s going to be high demand for vet techs for years to come.
This stems from how people consider animal care as part of their expenses.
This positive growth potential has made vet tech an ideal career choice.
Employment Growth Projection: 15%
2020
2030
That's a higher than average projected growth of 17,100: Interest Over Time
Should You Become a Vet Tech?

Overall Satisfaction: High
If you love animals, then this is a career you should very much consider.
To start, you must think of the following, especially when choosing a suitable specialization:
- Different types of vet tech jobs
- Types of animals you will work with

Average Salary: Medium
On average, a vet tech will make $31,800 a year.
Your salary will range from $21,890 to $47,410.
This is roughly $17.40 per hour, though this amount can vary depending on where you work.
The following factors will also affect your salary:
- Where you live
- The amount of experience you have
- Your certifications and licenses
- Vet tech specializations, if any

Job Growth Outlook: High
With the projected growth rate of 15% by 2030, vet techs won’t have to worry about not getting jobs.
They’re now in demand, leading animal care facilities to recruit them actively.
Think of it this way:
The more vet techs there are, the more animals get taken care of.
Education Duration: 2-3 Years
Schooling for vet tech programs is relatively shorter than others.
It lasts for two to three years wherein you have to secure an associate’s degree by then.
And if you would like to earn a specialization or go further in your education, it will take longer.

Personal Skills Needed
The number one criteria for being a vet tech is love and care for the animals’ health and welfare.
Other important personal skills are:
- Detail-oriented, where you need to check if everything is done correctly
- Can work under pressure, where you can keep a cool head in this demanding and stressful job
- Results-driven, where you strive to get the results you need
- Good communication skills, where you can get along with the people you work with, especially pet owners
- Strong resilience, where you can work and think fast in the face of emergencies
- Team-oriented, where you can work cohesively with your colleagues to achieve a goal
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How many years will it take to become a vet tech?
You only need an associate’s degree, which takes about two years to complete.
Q. How much do vet techs make?
On average, a vet tech will make $31,800 annually.
Eighty percent of them can earn anywhere from $21,890 to $47,410.
This is roughly $17.40 per hour.
However, this can still vary depending on:
- Where they live and work
- Years of experience
Q. What can you do with a vet tech degree?
Having a degree opens up a lot of opportunities for you, most especially when you pass the licensure exam.
You are able to work in a lot of environments.
For instance:
- Veterinary office, a common vet tech workplace
- Emergency animal hospital, where you can help animals in need of critical medical attention
- Research laboratory, where you can use animals for research
- Animal shelter, where you mostly help sick or injured animals
- Zoo, where you help veterinarians with emergency and routine care
Many technicians also use their degree as a starting point to another career, like:
- Veterinarian
- Veterinary technologist
- Veterinary specialist
- College professor
Q. What does a vet tech do every day?
A vet tech usually performs the following duties:
- Watch patients for behavior changes
- Prepare patients for surgery or exams
- Give patients first aid or nursing care
- Collect lab samples and test them
- Take x-rays and develop them
- Give treatments, shots, and medicine
- Collect and maintain patient records